Wet Stopping
What is tire tread depth?
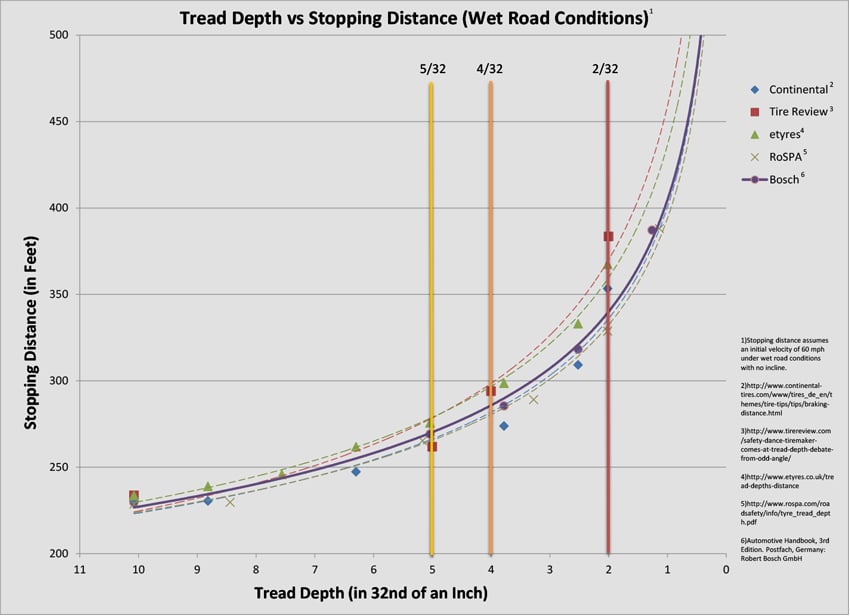
Tire tread depth is the measurement between the top of the tire and the tire's deepest grooves. Brand new tires are typically sold with 10/32" of usable tread depth, although this measurement can vary. As tires wear over time, tread depth decreases. In most US states, tires are legally worn out when tread depth reaches 2/32".
How does tread depth impact me?
Tire tread depth is important because a tire’s grooves squeeze out water, debris and snow so tires can hit the road and keep the vehicle running smoothly. As tires wear, the grooves become shallow and compromise the tire’s ability to make solid contact with the road. As tread depth decreases, the vehicle’s wet weather stopping distance increases. The video above shows just how drastically low tread depth can affect your vehicle’s ability to quickly and safely stop in wet weather conditions.
|
Inches
|
Millimeters
|
|
|
1/32
|
0.8
|
|
|
2/32
|
1.6
|
|
|
3/32
|
2.4
|
|
|
4/32
|
3.2
|
|
|
5/32
|
4.0
|
|
|
6/32
|
4.8
|
|
|
7/32
|
5.6
|
|
|
8/32
|
6.4
|
|
|
9/32
|
7.1
|
|
|
10/32
|
7.9
|
|
|
11/32
|
8.7
|
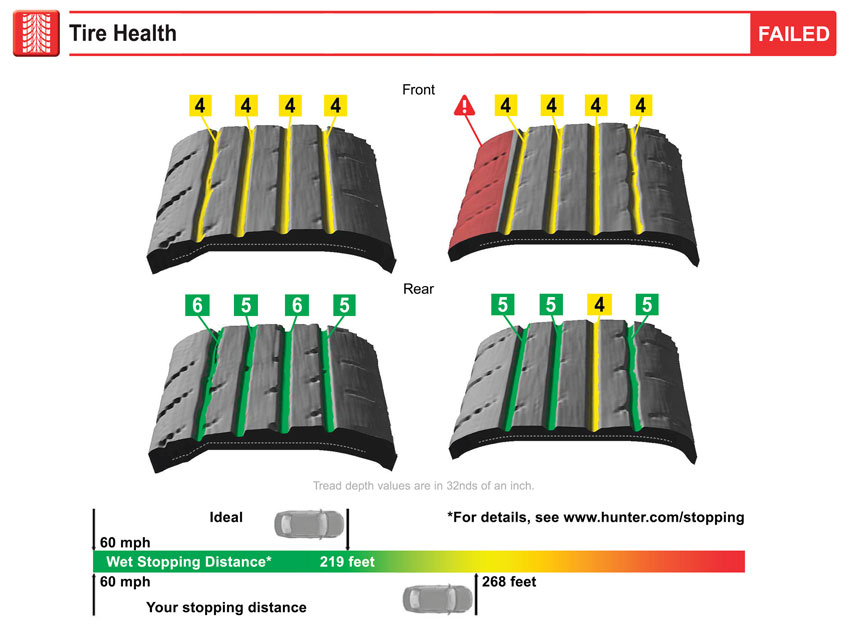
Actual tread depth measure and 3D model of tire tread displayed. 3D model of tire unique to each vehicle.
At this point in the stopping simulation your vehicle should stop in 230 feet.
We calculate that your vehicle will still be moving at 30 mph.
The tire and road conditions are such that the coefficient of friction between tire with a new set of tread and the road is 0.7. 0.7 is a fairly typical value for a wet (0.05" of water) asphalt road and normal tires. Some things that affect tire to road coefficient are tire rubber & road material, inflation, tread wear & pattern, smoothness or roughness of the road, amount of water or other materials on the road. Then the change in the coefficient of friction is calculated when only the tread depth is changed.
The simplified formula for wet weather stopping distance is:
S= V2 ∗ TD-0.25 / 9.5
S is Stopping distance in feet
V is Initial velocity in miles per hour
TD is tread depth in 32 of an inch
Various factors could increase or decrease the actual stopping distance:
- Driver reaction time
- Vehicle reaction time
- Max braking force being applied
- Decline or incline on road
- Mismatched treadwear or braking force
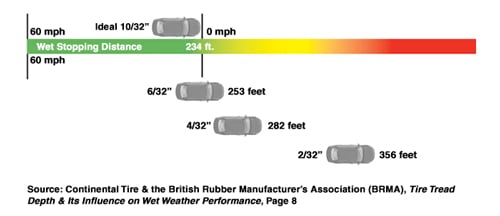
How is Wet Weather Stopping Distance calculated?
When calculating the minimum stopping distance, the following assumptions are being made:
- Initial velocity of 60 mph
- Driver & vehicle reaction time is instantaneous
- Max braking force is being applied on all 4 wheels
- No incline or decline on road
- Straight line stop
- No wheel lock-ups or hydroplaning
- Tire to road coefficient of friction is constant